Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming e-commerce by enabling smarter customer interactions, personalized shopping experiences, and data-driven marketing strategies. Recent reports show that a vast majority of marketers have already integrated AI into their operations – for instance, 69% of marketing teams were using AI tools by 2025 (iapp.org). From AI-powered chatbots providing instant customer support to algorithms that analyze consumer data for targeted advertising, AI offers e-commerce businesses powerful capabilities to optimize sales and customer satisfaction. However, alongside these opportunities come critical ethical considerations. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency in AI-driven decisions can erode customer trust if not properly addressed (iapp.orgcxtoday.com). This paper explores the types of AI “agents” and applications available to e-commerce platforms – including customer service bots, marketing analytics tools, and content generators – and outlines best practices for their ethical and effective use. The focus is on how online retailers can leverage AI responsibly for business intelligence and marketing, with an emphasis on transparency and human oversight at every step.
Figure 1 below summarizes major AI use case categories in e-commerce, ranging from customer experience to back-end operations. This breadth highlights that AI touches all aspects of online selling, though our discussion will concentrate on customer-facing and marketing applications.
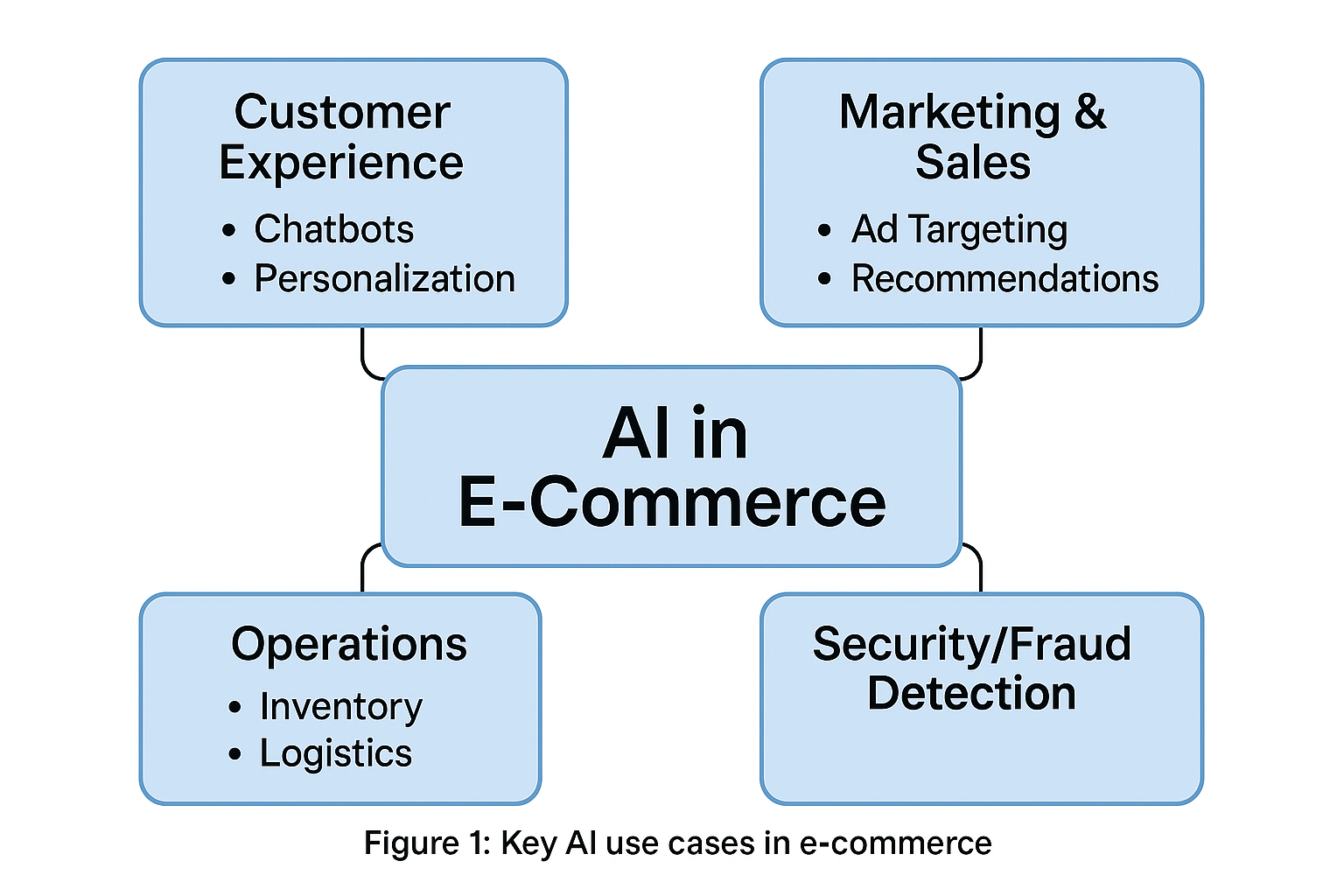
AI Agents Transforming the E-Commerce Experience
AI-Powered Customer Service: Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
One of the most visible AI applications in e-commerce is the use of chatbots and virtual assistants to handle customer service and sales inquiries. These AI agents employ natural language processing to simulate conversation and help customers in real time (research.aimultiple.com). Deployed on websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms, chatbots can address frequently asked questions, assist with product selection, and even guide customers through the checkout process without human intervention. The benefits are significant: an AI chatbot offers 24/7 service availability across multiple channels, meaning customers can get help at any time of day without waiting for a human agent (cxtoday.com). These bots can engage in unlimited simultaneous conversations, providing instant responses to routine queries and thus freeing up human staff to focus on more complex issues (cxtoday.com). Not only do they reduce wait times, but they can also leverage customer data (order history, browsing behavior) to personalize their interactions. For example, if a customer asks a chatbot for product recommendations, the AI can analyze that customer’s past purchases or preferences to suggest relevant items, mimicking a personalized shopping assistant (cxtoday.com).
Advanced virtual customer assistants (VCAs) take things a step further. Often used in e-commerce mobile apps and smart devices, VCAs combine voice recognition and natural language understanding to perform complex tasks via conversation (ibm.com). A virtual agent can handle actions like placing orders, checking account status, or offering detailed product advice just as a human sales representative would (ibm.com). These AI assistants are becoming more “human-like” in their interactions by using contextual understanding and even sentiment analysis to respond appropriately to customer emotions (cxtoday.comibm.com). In practice, this could mean an AI assistant that detects frustration in a customer’s messages and proactively offers to escalate the issue or provide a discount. Importantly, successful e-commerce deployments ensure that AI support augments rather than replaces the human touch. Even as AI handles routine inquiries, customers are given a clear path to reach a human agent whenever needed (for instance, by typing “human” or pressing 0) (cxtoday.com). Maintaining this “human-in-the-loop” option is crucial: it guarantees that complex or sensitive situations can be addressed with human empathy, and it prevents customers from feeling trapped with an unhelpful bot (cxtoday.com).
The improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction from AI-driven service are well documented. By instantly resolving common questions (e.g. about shipping, returns, product details), AI assistants shorten support response times and increase first-contact resolution rates (ibm.comresearch.aimultiple.com). Some companies have reported double-digit percentage drops in call handling times after implementing AI chatbots, as routine queries no longer clog up call queues (ibm.com). Moreover, voice-based AI agents can handle phone inquiries with speech recognition, further extending omnichannel support (cxtoday.com). Ultimately, AI-powered customer service – when implemented with proper oversight – becomes a competitive advantage for e-commerce: it provides scalable, always-on assistance that improves the shopping experience, fosters loyalty, and reduces operational costs (ibm.comcxtoday.com). The key is to deploy these agents thoughtfully, with clear benefits to customers and fail-safes (like human backup and data security) to mitigate any risks.
Personalized Recommendations and Shopping Experiences
In e-commerce, personalization is king – customers are more likely to engage and convert when they receive product recommendations, promotions, and content tailored to their interests. AI algorithms excel at this kind of personalization by analyzing large volumes of customer data to discern patterns and preferences. Recommendation engines are a prime example: these AI systems learn from each user’s browsing behavior, past purchases, and even demographic data to suggest products that the user is likely to be interested inresearch.aimultiple.com. Many major online retailers deploy AI recommendation engines on their websites (“Recommended for you” sections) and in marketing emails to increase cross-sells and upsells. By crunching data on what similar customers have viewed or bought, the AI can highlight, for instance, a popular nursing pillow cover to someone who has just added a nursing pillow to their cart – thus increasing the average order value through smart suggestions.
AI-driven personalization isn’t limited to product recommendations. It also powers dynamic content on e-commerce sites, such as showing different homepage banners or search results to different customer segments based on their profiles. For example, an AI system might learn that one segment of visitors is price-sensitive and automatically highlight items on sale to them, while showing new arrivals to another segment that values the latest products. Through machine learning models, e-commerce platforms can create these hyper-segmented experiences that go beyond one-size-fits-all merchandising. According to industry research, such AI personalization is revolutionizing the online shopping journey by making it more relevant and satisfying for each customercotinga.io. Shoppers receive timely, curated suggestions that feel intuitive rather than random, which can significantly drive engagement and repeat purchasescotinga.iocotinga.io.
Of course, this level of personalization is fueled by customer data – which raises privacy considerations that we will discuss later. Ethical use of AI for personalization means using data responsibly and with transparency (e.g. obtaining proper consent and allowing users to adjust preferences). Nonetheless, when done right, personalization via AI benefits both customers and retailers: customers enjoy a more convenient experience finding what they need, and retailers see higher conversion rates and loyalty due to more satisfied shopperscotinga.ioresearch.aimultiple.com. Notably, these AI systems continuously learn and adapt; as they gather more data over time, their recommendations become more accurate. Many e-commerce companies combine this with AI-driven inventory management – ensuring that recommended items are in stock and optimizing stock levels based on predicted demand for certain productscotinga.iocotinga.io. In summary, AI agents acting behind the scenes to personalize content and manage inventory contribute to a smoother, more responsive e-commerce experience, akin to a personal store assistant for every customer, at scale.
AI in Digital Marketing and Advertising
Beyond customer-facing storefronts, AI is also transforming how e-commerce companies approach digital marketing and advertising. Modern online advertising platforms (such as Google Ads and social media ads) heavily incorporate machine learning to optimize campaign performance. For instance, AI algorithms automatically adjust ad bidding, targeting, and placements in real time to maximize click-through and conversion rates under a given budget. E-commerce marketers can leverage AI-driven tools to segment audiences more precisely and create hyper-targeted campaigns. Predictive analytics models analyze historical customer data and behaviors to forecast future trends, enabling marketers to anticipate seasonal demand shifts or identify emerging customer segments (professional.dce.harvard.eduprofessional.dce.harvard.edu). By crunching vast datasets far beyond human capacity, AI provides real-time insights that help adjust marketing strategies on the fly – ensuring the right products are advertised to the right people at the right time (professional.dce.harvard.edu). For example, if an AI model detects that a certain baby product is suddenly trending in social media sentiment, a retailer can quickly ramp up promotions for that item. This data-driven agility can yield greater return on investment and keeps e-commerce brands competitive in fast-changing markets (professional.dce.harvard.eduprofessional.dce.harvard.edu).
AI is also making its mark in content creation for marketing. The advent of powerful generative AI (like GPT-4 and other large language models) has enabled e-commerce marketers to automate the production of ad copy, product descriptions, blog posts, and even imagery. Marketers can now prompt AI tools with specific instructions or keywords and receive draft text for a product page or a set of social media captions within seconds (professional.dce.harvard.edu). These AI-generated contents can be tuned to match the brand’s tone and optimized for SEO or conversion, significantly boosting productivity for marketing teams. For instance, an e-commerce site could use AI to generate a first draft of a blog article about “How to choose the best nursing pillow,” then have a human editor refine it (a process we will revisit under human oversight). AI image generation models can similarly create visual assets – for example, producing varied background scenes or color variants for product photos without needing an in-house photographer (professional.dce.harvard.edu). This capability to scale content creation helps smaller e-commerce businesses compete in content marketing, as they can produce rich product information and marketing materials quickly with minimal cost.
However, using AI in marketing content also introduces risks such as the generation of inaccurate or biased information (hallucinations) and potential infringement on intellectual property if the AI output inadvertently copies existing material (iapp.org). Therefore, it is considered best practice that any AI-generated ad or copy must be reviewed by a human before publication – a topic we detail in the best practices section. Many forward-thinking companies have instituted internal guidelines that no AI-generated content goes live without human approval, ensuring factual accuracy and brand integrity are preserved (iapp.org).
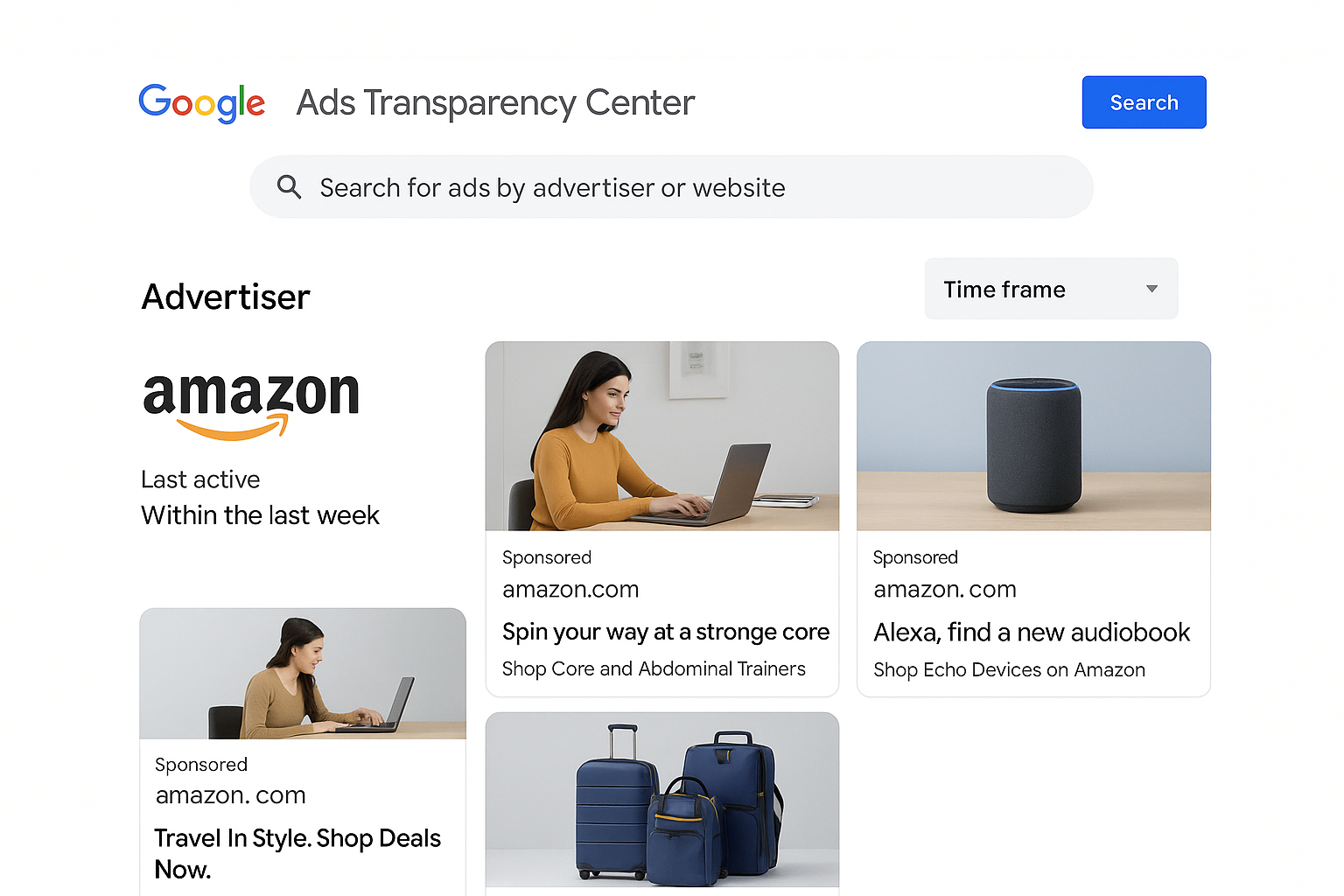
Another critical aspect of marketing where AI plays a role is competitive intelligence and transparency. Marketers can ethically gather insights on competitors’ advertising strategies using tools like Google’s Ads Transparency Center. In 2023, Google launched this public transparency portal (also known as the Google Ads Library) to let anyone search for ads running on Google’s network by advertiser name or website (digitalsqueak.co.zadigitalsqueak.co.za). Through this interface, an e-commerce business can look up a competing brand and see samples of their active ads, including the ad copy, creatives, and how recently those ads ran. This is a game-changer for market research: it allows “spying” on competitor ads in a legitimate, transparent way that Google encourages as part of an open advertising ecosystem (singlegrain.comsinglegrain.com). Marketers can use these insights to inform their own campaigns – for example, noting what messaging or imagery a rival is using for nursing pillow ads and then differentiating their own approach or finding inspiration for new ad angles. The Google Ads Transparency Center provides features to filter ads by date range, format (text, image, video), and location, giving a historical view of competitors’ advertising activities (singlegrain.comsinglegrain.com). It is important to emphasize that this kind of competitor analysis is ethical and recommended: rather than engaging in any deceptive data scraping, marketers are relying on a publicly available transparency tool provided by Google to ensure accountability in advertising (singlegrain.com). Using the transparency center aligns with ethical marketing practices because it levels the playing field and discourages dishonest ads – knowing that all ads are publicly viewable encourages companies to be truthful and fair in their advertising. The information gleaned (such as a competitor’s core messaging or promotion frequency) can be folded into an e-commerce firm’s business intelligence to refine their marketing strategy.
Figure 2: Google’s Ads Transparency Center interface, which allows users to search and view active ads by advertiser or website. This tool is part of Google’s initiative to enhance transparency and accountability in digital advertising (singlegrain.com). E-commerce marketers can leverage it to study competitors’ ads (e.g., creative content, messaging, formats) over different time frames, helping inform their own ethical advertising strategies.
AI for Analytics and Business Intelligence
E-commerce companies generate enormous amounts of data – from website clickstreams and customer demographics to sales transactions and social media feedback. AI systems are uniquely suited to analyze this “big data” and extract actionable business intelligence. One common application is demand forecasting: machine learning models ingest historical sales figures, web traffic patterns, marketing campaign data, and even external factors (like seasonality or economic indicators) to predict future product demand with high accuracy (professional.dce.harvard.eduprofessional.dce.harvard.edu). These AI-driven forecasts enable retailers to optimize inventory levels – ensuring they have enough stock of popular items and reducing overstock of slow sellers – and to make informed decisions on purchasing and supply chain management. By avoiding stockouts of in-demand products and minimizing excess inventory, companies can both improve revenue and reduce waste. For example, an AI forecast might reveal an expected surge in demand for infant feeding products in a certain month, prompting the business to stock up and prepare targeted promotions for that period.
AI analytics also power customer segmentation and lifetime value analysis. By clustering customers based on their behaviors and attributes, AI can help e-commerce marketers identify, say, a segment of high-value repeat customers versus one-time bargain shoppers, and tailor different strategies for each. Predictive models can score leads or customers on their likelihood to convert or churn, allowing businesses to proactively engage those who might lapse (professional.dce.harvard.eduprofessional.dce.harvard.edu). This kind of insight takes the guesswork out of marketing decisions – budgets can be allocated more efficiently by focusing on the most promising customer groups or products. In fact, AI-driven lead scoring and personalization can even operate in real-time: as soon as a user interacts with a website or email, algorithms adjust the content or offers shown to maximize the chance of purchase (professional.dce.harvard.edu).
Another analytical use case is sentiment analysis and social listening. AI tools can comb through customer reviews, survey responses, or social media posts to gauge public sentiment about a brand or product (cxtoday.com). By understanding common themes in customer feedback – e.g., identifying that many users find a pillow product “too firm” or customer service “very responsive” – e-commerce companies can quickly address pain points and capitalize on strengths. These sentiment insights, delivered via AI dashboards, feed into product development and marketing messaging, ensuring the business is **aligned with customer needs and perceptions】(cxtoday.com). AI can even alert teams to emerging issues (like a sudden spike in negative sentiment after a product update) so they can perform damage control promptly.
Crucially, AI-enabled business intelligence should be used to augment human decision-making, not replace it. The role of these analytics tools is to sift data and highlight patterns that humans may miss, but it still requires human judgment to interpret why those patterns exist and what actions to take. For instance, if an algorithm finds that a certain advertisement is performing poorly with a specific demographic, a marketing manager will need to hypothesize whether the content failed to resonate or if it was shown in the wrong context. Combining the speed and data-crunching power of AI with human critical thinking leads to the best outcomes (ibm.com). Companies are finding that embedding AI insights into their strategic planning increases agility – they can respond to market changes in near real time – while humans ensure these responses make business sense and align with the brand’s values (ibm.comprofessional.dce.harvard.edu).
Best Practices for Ethical AI Use in E-Commerce
While AI offers transformative benefits for e-commerce, it must be adopted responsibly. In this industry – as in others – ethical AI usage is not just a nicety but a necessity to maintain customer trust and comply with regulations. Below, we outline key best practices and principles to guide e-commerce companies in deploying AI for customer service, marketing, and analytics in an ethical manner. These practices ensure that AI augments business objectives without compromising on transparency, fairness, or accountability.
- Develop Clear AI Ethics Policies: Organizations should start by establishing a formal AI ethics policy or guidelines. This policy defines how AI will be used in alignment with the company’s values, legal requirements, and customer expectations (cxtoday.com). It should cover areas like data usage, bias prevention, and oversight. By having a code of conduct for AI, businesses create internal awareness and accountability for ethical issues. For example, an AI policy may mandate that models undergo bias testing before deployment, or that AI-generated content must be labeled and reviewed. Investing in such AI governance upfront ensures long-term sustainable AI adoption (cotinga.iocotinga.io).
- Prioritize Data Privacy and Security: AI systems often rely on large datasets – including personal customer information – to learn and make decisions. E-commerce firms must handle this data with utmost care. That means complying with privacy laws (like GDPR or CCPA), obtaining consent where required, and minimizing data collection to only what is necessary (cotinga.iocotinga.io). Techniques such as data anonymization or federated learning can be employed to train AI models without exposing individual identities (cotinga.io). Robust security measures (encryption, access controls) are non-negotiable to protect data from breaches (cotinga.io). Being transparent with users about data practices is also key: customers should know what data is collected for AI personalization and have options to opt out if they desire. By safeguarding privacy, companies not only avoid legal pitfalls but also build trust with their audience.
- Ensure Transparency and Explainability: Transparency in AI usage entails being open with consumers and stakeholders about when and how AI is impacting decisions. E-commerce companies should disclose, wherever appropriate, that an interaction or piece of content was AI-assisted. For instance, if a chatbot is AI-driven, the interface can clarify that (e.g., “Virtual Assistant”) rather than pretending to be a human agent. According to experts, letting customers know AI is being used – and being clear about how their data is handled – “helps build trust and keeps the experience respectful and responsible” (ibm.com). Transparency also extends to explaining AI-driven outcomes in understandable terms. If an AI recommendation engine suggests products or sets dynamic prices, the company should be prepared to explain the general logic (without revealing proprietary algorithms) to any customer or regulator who asks. Using explainable AI (XAI) techniques can help provide reasons for recommendations (for example, “recommended because you purchased X”). Overall, transparency acts as a safeguard against mistrust: it shows the company has nothing to hide and is using AI in good faith (cotinga.iocotinga.io).
- Mitigate Bias and Ensure Fairness: AI models can inadvertently perpetuate bias present in training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes – an issue of particular concern in marketing and customer treatment (iapp.org). For e-commerce, this could manifest in ways like an AI ad platform showing higher-end product ads predominantly to one demographic and not another, or a chatbot failing to understand certain dialects or phrases, frustrating a subset of users. To avoid such scenarios, companies must actively work to identify and eliminate bias in their AI systems. Best practices include using diverse, representative training data, conducting regular audits of AI outputs for biased patterns, and using tools for bias detection (e.g., Google’s Dataset Search or IBM’s AI Fairness 360 toolkit) (iapp.orgiapp.org). If biases or “hallucinations” (AI-generated false content) are detected, there should be processes to correct the AI’s course – such as retraining the model on improved data or adjusting its algorithms (iapp.orgiapp.org). Importantly, ethics policies should explicitly forbid uses of AI that could lead to unlawful discrimination or sensitive decisions without human oversight. For example, an AI should not be solely responsible for deciding on personalized pricing or discounts that might inadvertently redline certain groups, unless carefully vetted for fairness. Striving for fairness isn’t just ethically right; it also protects the business from reputational harm and fosters an inclusive customer base.
- Keep Humans in the Loop for Oversight: Human oversight is an overarching principle that applies to all the above points. No matter how advanced AI systems become, e-commerce companies should maintain a “human in the loop” to supervise and guide AI decisions, especially in customer-facing functions. In practice, this means two things: operational oversight and content oversight. For operational decisions (like handling an escalated customer issue or approving a refund flagged by AI), always allow a human agent to review and override the AI’s recommendation when appropriate (cxtoday.com). AI customer service bots, as noted, should seamlessly hand off to human staff upon customer request or when queries fall outside the bot’s competence. This human fail-safe ensures edge cases or emotionally sensitive situations are dealt with properly by a person. For marketing content, human oversight means having staff edit and approve AI-generated material – whether it’s a product description, a blog post, or an advertisement – before it goes live (iapp.org). A human can catch factual errors, tone issues, or culturally insensitive language that an AI might miss. Many organizations are formalizing this by instituting checkpoints in their AI content workflows. For example, Salesforce (a leader in marketing technology) has implemented a policy of “mindful friction,” introducing deliberate pauses in the AI content generation process to require human review at critical junctures (iapp.org). This kind of built-in oversight ensures that AI augments creative work without running unchecked. As another example, Unilever’s AI ethics policy mandates that any decision with a significant impact on someone’s life “should not be fully automated” (iapp.org), underscoring the need for human judgment in consequential decisions. While selling a product online may not be a life-altering decision, the spirit of these policies is highly relevant – important decisions in customer experience or strategy should involve human approval. By keeping humans in the loop, e-commerce businesses maintain accountability: there is always a responsible person who can explain and stand behind the outcome, rather than blaming a “black box” algorithm. Human oversight also provides an avenue for consumers to seek recourse – for instance, a customer dissatisfied with an AI-generated response can have their issue reviewed by a human manager, preserving trust that the company cares about the customer’s experience.
- Accountability and Continuous Monitoring: Ethical AI use is not a one-and-done checklist but an ongoing commitment. E-commerce companies should set up mechanisms to continuously monitor AI system performance and its alignment with ethical standards (cxtoday.comcotinga.io). This could involve periodic audits of AI decisions (for fairness, accuracy, relevance), user feedback loops to learn about any AI missteps, and keeping abreast of evolving regulations or industry norms. Assigning clear accountability is important – for example, having a designated AI ethics officer or taskforce that reviews AI deployments and addresses any incidents. If an AI tool makes a mistake (say, a pricing algorithm error or a chatbot misunderstanding that goes viral on social media), the company should take responsibility transparently and use the incident as a learning opportunity to tighten the system. Internally, training employees on how to appropriately use AI tools is part of accountability. Staff should understand the limitations of AI, know how to verify AI outputs, and be encouraged to question the AI’s recommendations if something seems off (iapp.orgiapp.org). By creating a culture where AI is a tool under human direction – not an infallible oracle – companies can avoid over-reliance on automation and ensure that ethical principles guide every AI-driven action.
The Role of Transparency Tools in Ethical Marketing
An important aspect of ethical AI and marketing is leveraging tools that promote transparency in the industry as a whole. We touched on the Google Ads Transparency Center earlier as a means for competitor analysis. It’s worth revisiting this in the context of broader transparency and fairness in advertising. Google’s Ads Transparency Center was introduced as part of a push for more open and accountable advertising ecosystems (singlegrain.com). The tool essentially makes the digital ad space less opaque: consumers, regulators, and advertisers themselves can see what ads are running, by whom, and gain some insight into targeting criteria. For e-commerce businesses, using this tool serves a dual purpose – strategic intelligence and ethical assurance. Strategically, it helps businesses remain informed about their competitors’ marketing moves in a legitimate way, as discussed. Ethically, it encourages companies to hold themselves to high standards; knowing that one’s ads are publicly viewable discourages misleading advertising or dark patterns. Companies can also use the transparency center to audit their own ads, ensuring that the messages align with their ethical commitments (for example, checking that no ad is inadvertently making a claim that could be seen as deceptive or that all ads properly include any required disclosures).
Beyond Google’s platform, other tech giants have similar transparency efforts (for instance, Facebook/Meta’s Ad Library for social ads). E-commerce marketers should make it routine to review such libraries. Doing so not only guides better marketing tactics but also signals participation in an industry culture that values openness. In an era where consumers are increasingly concerned about manipulative ads and misuse of personal data, being able to say “we welcome transparency and comparison, and we strive to compete on honest messaging and value” becomes part of a brand’s ethical narrative. Transparency tools can also reveal industry advertising trends – if most competitors are highlighting sustainability or ethical sourcing in their ads, it might indicate shifting consumer values that your business should also address authentically. In summary, the use of transparency tools is a best practice in its own right, reinforcing ethical marketing by aligning business intelligence gathering with the principles of fairness and openness that benefit everyone in the ecosystem.
Conclusion
AI technologies offer exciting possibilities for e-commerce companies to enhance customer service, personalize shopping, and sharpen their marketing – all leading to improved business performance. From intelligent chatbots that provide round-the-clock assistance to analytics engines that predict trends, these AI “agents” are becoming integral across online selling platforms large and small. The nursing products sector, like any retail niche, stands to gain from these tools in engaging and supporting customers more effectively and in making data-informed decisions. Yet, as we have outlined, harnessing AI’s power must go hand-in-hand with a commitment to ethics and transparency. E-commerce businesses have a responsibility to use AI in ways that respect customer privacy, treat users fairly, and are transparent about how AI influences the customer experience. Adhering to best practices such as rigorous privacy protection, bias mitigation, clear disclosure of AI use, and maintaining human oversight at key decision points will help ensure that AI augments trust rather than undermines it.
By fostering transparency, fairness, and human oversight, companies can align AI-driven operations with both consumer expectations and societal values (iapp.org). In practical terms, this means customers should never feel deceived or powerless when interacting with AI on an e-commerce site – rather, they should benefit from faster service, useful recommendations, and relevant ads that AI enables, all while knowing their rights and preferences are respected. When AI is deployed thoughtfully, with ethical guardrails, it becomes a powerful ally for both the business and its customers. It streamlines shopping and support in a manner that feels helpful and personalized, not invasive or biased. As AI continues to evolve, e-commerce platforms that prioritize responsible AI adoption will be best positioned to innovate and retain customer loyalty. They will leverage AI for its strengths – efficiency, scalability, insight – but always under human guidance and aligned with a strong ethical compass. In doing so, these companies demonstrate that technology and ethics can advance hand in hand, driving success in the marketplace while upholding the trust and values that sustain long-term customer relationships.
References: (Selected)
- Harvard DCE Professional Development (2024). How AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – on generative AI in marketing and ethical considerationsprofessional.dce.harvard.eduprofessional.dce.harvard.edu.
- IBM Consulting (2025). AI in Customer Service – emphasizing human-AI collaboration and transparency to customersibm.com.
- IAPP (2025). The Ethical Use of AI in Advertising – discussing adoption stats and need for transparency, fairness, oversight in AI-driven marketingiapp.orgiapp.org.
- CX Today (2023). AI Customer Support Best Practices – highlighting 24/7 chatbots, ethical AI policies, and keeping humans in the loop in support contextscxtoday.comcxtoday.com.
- Google Ads Transparency Center – industry articles explaining its features for viewing competitors’ ads as part of Google’s transparency initiativesinglegrain.comdigitalsqueak.co.za.
Citations
The ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPP
https://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI eCommerce: 25 Use Cases to Optimize Sales and CXhttps://research.aimultiple.com/ai-e-commerce/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI eCommerce: 25 Use Cases to Optimize Sales and CXhttps://research.aimultiple.com/ai-e-commerce/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI eCommerce: 25 Use Cases to Optimize Sales and CXhttps://research.aimultiple.com/ai-e-commerce/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI eCommerce: 25 Use Cases to Optimize Sales and CXhttps://research.aimultiple.com/ai-e-commerce/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/The ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingHow to Use the Google Ads Library to Spy on Competitorshttps://digitalsqueak.co.za/how-to-use-the-google-ads-library-to-spy-on-competitors/How to Use the Google Ads Library to Spy on Competitorshttps://digitalsqueak.co.za/how-to-use-the-google-ads-library-to-spy-on-competitors/Google Ads Transparency: Insights & Features Guidehttps://www.singlegrain.com/blog/ms/google-ads-transparency/Google Ads Transparency: Insights & Features Guidehttps://www.singlegrain.com/blog/ms/google-ads-transparency/Google Ads Transparency: Insights & Features Guidehttps://www.singlegrain.com/blog/ms/google-ads-transparency/Google Ads Transparency: Insights & Features Guidehttps://www.singlegrain.com/blog/ms/google-ads-transparency/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceAI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/The ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingAI Customer Support: The Use Cases, Best Practices, & Ethics – CX Todayhttps://www.cxtoday.com/contact-center/ai-customer-support-the-use-cases-best-practices-ethics/AI in E-Commerce: Ethical Considerations and Best… – Cotingahttps://cotinga.io/blog/ai-in-e-commerce-ethical-considerations-and-best-practices/The ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingThe ethical use of AI in advertising | IAPPhttps://iapp.org/news/a/the-ethical-use-of-ai-in-advertisingAI Will Shape the Future of Marketing – Professional & Executive Development | Harvard DCEhttps://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-marketing/AI in Customer Service | IBMhttps://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-customer-serviceHow to Use the Google Ads Library to Spy on Competitorshttps://digitalsqueak.co.za/how-to-use-the-google-ads-library-to-spy-on-competitors/